The first and second laws of thermodynamics
Fondamental : Definition of the internal energy
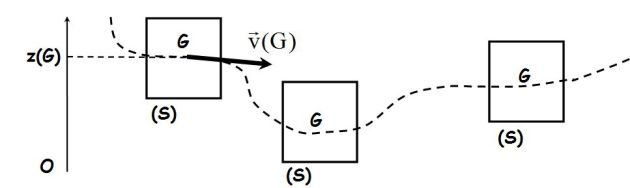
Consider a thermodynamic system \((S)\) at rest in the laboratory reference (R) (gas in a vessel, solid, ...).
The internal energy is a state function of a system : it is defined in the equilibrium state of the thermodynamic system.
\(U = \sum\limits_{Particles} {{e_{{c_i}}}} \;\;\;\;+\;\;\;{E_{p,{\mathop{\rm mut}} \;int}}\)
Sum of microscopic kinetic energies of the system constituents and of the potential energy of mutual interaction between the constituents.
It is a function of the system state variables.
If the system (with masse \(M_{tot}\)) is in movement in (R), the mechanical energy \(E_m\) will then take into account the macroscopic kinetic energy and macroscopic gravitational potential energy :
\({E_m} = \;\;U\; +\;\frac{1}{2}{M_{tot}}v{(G)^2}\; +\;{M_{tot}}g\;z(G)\)
Where \(G\) is the center of inertia of the system.
Fondamental : Statement of the first law
Consider a closed and motionless thermodynamic system \((S)\) in the laboratory frame (R).
This system undergoes a transformation in which its internal energy varies :
\(\Delta U=U_f-U_i\)

This variation is due to two contributions :
To the work \(W\) of forces (pressure, for example) that act on the system \((S)\).
To heat transfer (amount of heat) \(Q\) received by the system \((S)\).
The first law of thermodynamics is the law of conservation of energy :
\(\Delta U = {U_f} - {U_i} = W + Q\)
For an elementary transformation (reversible or quasi-static) :
\(dU = \delta W + \delta Q\)
If the system \((S)\) is driven by an ensemble movement which respects to the laboratory frame (R) :
\(\Delta \left( {U + \frac{1}{2}{M_{tot}}v{{(G)}^2} + {M_{tot}}g\;z(g)} \right) = W + Q\)
Fondamental : Special transformations
Pure thermal transformation (\(W = 0\)) :
\(\Delta U=Q\)
Adiabatic transformation (\(Q = 0\)) :
\(\Delta U=W\)
Cyclic transformation (suite of transformations during which the system returns to its original state) :
\((\Delta U )_{cycle}= (W+Q)_{cycle}=0\)
Fondamental : Statement of the second law of thermodynamics
A fun video : "Entropy viewed by The Shadoks"
Entropy is a state function, additive and extensive.
Elementary expression of 2nd law :
The system receives work and heat \(\delta Q\) from a heat source of temperature \(T_{ext}\).
Its variation of entropy \(dS\) verifies :
\(dS \ge \frac{{\delta Q}}{{{T_{ext}}}}\)
What is written in the form :
\(dS = \frac{{\delta Q}}{{{T_{ext}}}} + \delta {S_{creation}} = \delta {S_{exchange}} + \delta {S_{creation}}\)
With :
\(\delta {S_{exchange}} = \frac{{\delta Q}}{{{T_{ext}}}}\;\;\;\;\;and\;\;\;\;\;\delta {S_{creation}} \ge 0\)
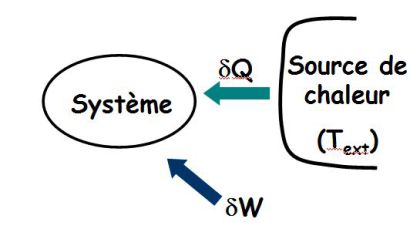
\(\delta S_{exchange}\) : entropy of exchange depends on the heat exchange with the outside ; its sign is arbitrary.
\(\delta S_{creation}\) : the entropy of creation (positive or zero, only in the case of a reversible transformation) is related to the internal transformation within the system and characterizes the degree of irreversibility of the transformation (heterogeneity of temperature, concentrations, pressure disequilibrium, ...).
Expression of the 2nd principle to a finite transformation :
The system receives work and heat from a heat source of temperature \(T_{ext}\).
Its entropy variation \(\Delta S\) verifies :
\(\Delta S \ge \int_{EI}^{EF} {\frac{{\delta Q}}{{{T_{ext}}}}}\)
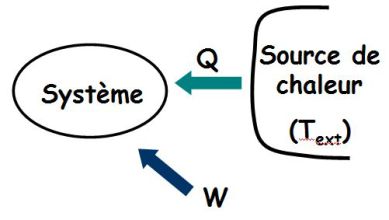
What is written in the form :
\(\Delta S = \int_{EI}^{EF} {\frac{{\delta Q}}{{{T_{ext}}}}} + {S_{creation}} = {S_{exchange}} + {S_{creation}}\)
With :
\({S_{exchange}} = \int_{EI}^{EF} {\frac{{\delta Q}}{{{T_{ext}}}}} \;\;\;\;\;and\;\;\;\;\;{S_{creation}} \ge 0\)
Méthode : In practice, how to realize an entropy balance ?
Calculating \(\Delta S\) :
Is calculated by imagining a reversible transformation bringing from the same IS (Initial Sate) to the same FS (Final Sate) or directly if we know the entropy function (perfect gas, for example).
Calculating \(S_{exchange}\) :
\({S_{exchange}} = \int_{EI}^{EF} {\frac{{\delta Q}}{{{T_{ext}}}}}\)
is calculated on the path really followed.
Calculating \(S_{creation}\) :
Then calculates :
\({S_{creation}} = \Delta S - {S_{exchange}} \ge 0\)
If the transformation is reversible (with \(T_{ext}=T\)) :
\(\Delta S = {S_{exchange}} = \int_{EI}^{EF} {\frac{{\delta Q}}{T}} \;\;\;\;\;and\;\;\;\;\;{S_{creation}} =0\)
Exemple : An example of entropy balance
Hot metal is placed at temperature \(T_1\) (mass \(m\), specific heat capacity \(c_m\)) in the pool water at constant temperature \(T_0 <T_1\).
Make an entropy balance.
Calculate the change in entropy of metal (incompressible phase) :
\(\Delta {S_{metal}} = m{c_m}\ln \left( {\frac{{{T_0}}}{{{T_1}}}} \right)\)
Entropy of exchange is calculated on the path really followed :
\({S_{exchange}} = \int_{EI}^{EF} {\frac{{\delta Q}}{{{T_{ext}}}}} = \frac{{m{c_m}({T_0} - {T_1})}}{{{T_0}}}\)
We deduce the entropy of creation :
\({S_{creation}} = m{c_m}\ln \left( {\frac{{{T_0}}}{{{T_1}}}} \right) - \frac{{m{c_m}({T_0} - {T_1})}}{{{T_0}}}\)
Or again :
\({S_{creation}} = m{c_m}\left[ {\frac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_0}}} - 1 - \ln \left( {\frac{{{T_1}}}{{{T_0}}}} \right)} \right] > 0\)
Fondamental : Entropy of an ideal gas
In variables \(T\) and \(V\) (for \(n\) moles) :
\(S(T,V) = n\frac{1}{{\gamma - 1}}R\ln (T) + nR\ln (V)\; + cste\)
In variables \(T\) and \(P\) (for \(n\) moles) :
\(S(T,P) = n\frac{\gamma}{{\gamma - 1}}R\ln (T) - nR\ln (P)\; + cste\)
With :
\(\gamma = \frac {C_P}{C_V}\).
Complément : Statistical interpretation of entropy
Does the entropy of a student's office look like the one of the left office or the one of the right office ?
If we call \(\Omega\) the number of microscopic states accessible by the macroscopic system, then the entropy can be written as :
\(S=k_B\;ln\Omega\)
where \(k_B\) is the Boltzmann constant.
Finally, a system will be all the more disorderly as its entropy is big.
In particular, when changing from liquid state to gas, for example, the entropy will increase as the gas state is less ordered than the liquid state.